Suhail Bashir Peer: Climate change is the long-term alteration of temperature and weather patterns on Earth. It is caused by the release of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming of the planet’s surface and atmosphere. The primary human activity that contributes to climate change is the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and gas, for energy.
Climate change has a wide range of impacts on the planet, including rising sea levels, more frequent and severe extreme weather events, changes in precipitation patterns, and shifts in the distribution of plant and animal species. It also exacerbates existing environmental and social issues, such as air pollution, water scarcity, and food insecurity.
South Asia’s annual monsoon brings life-giving water to nearly a quarter of humanity. But climate change is making the monsoon more erratic, less dependable and even dangerous, with more violent rainfall as well as worsening dry spells. https://t.co/Q6uYLlzlhw pic.twitter.com/5ETTU8w1pu
— The New York Times (@nytimes) October 5, 2022
South Asia is one of the regions in the world that is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change due to high diversity and fragile ecosystems. The region is characterized by a high population density, a large proportion of poor and marginalized communities, and a high dependence on natural resources. Climate change is expected to have a wide range of impacts on South Asia, including:
- Increasing temperatures: South Asia is likely to experience an increase in average temperatures, which can lead to heat stress, crop failures, and water shortages.
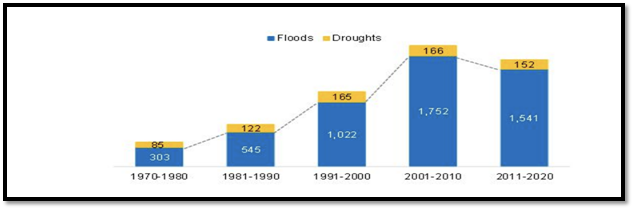
- Floods and droughts: The region is already prone to floods and droughts, and climate change is expected to exacerbate these extreme weather events, leading to crop failures and water shortages.
- Sea level rise: Coastal areas in South Asia are at risk of flooding and erosion due to sea level rise, which can displace millions of people and damage infrastructure.
- Changes in precipitation: Climate change is expected to lead to changes in precipitation patterns, with some areas experiencing more intense monsoons and others experiencing more prolonged droughts.
- Loss of biodiversity: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are likely to lead to the loss of biodiversity and the degradation of ecosystems in South Asia.
- Increase in frequency and intensity of natural disasters: South Asia is already prone to natural disasters such as cyclones, floods, and droughts. Climate change will lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of such natural disasters.
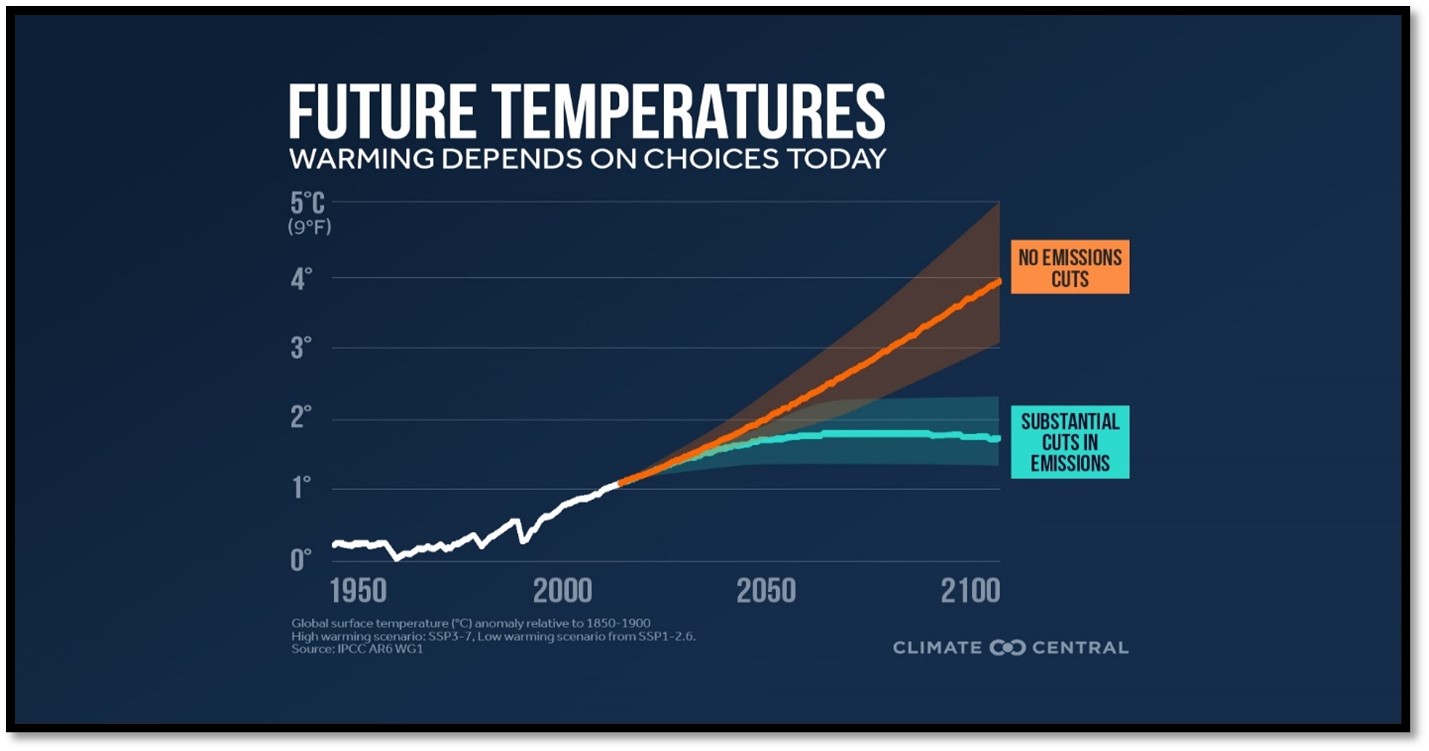
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) predicts that if greenhouse gas emissions are not reduced, global average temperatures are likely to increase by 1.5 to 4.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 to 8.1 degrees Fahrenheit) by the end of the century.
This could have devastating effects on the planet, including more severe droughts, heat waves, hurricanes, and flooding. It would also lead to the extinction of many plants and animal species and cause significant damage to human health and livelihoods.
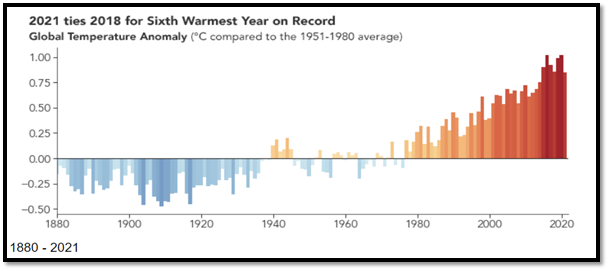
It was observed and reported by NASA and NOAA, Earth’s global average surface temperature in 2021 tied with 2018 as the sixth-warmest year on record and the past eight years have been the warmest since modern recordkeeping began in 1880. The significant increase trend is consistent with the long-term irreversible warming trend caused by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation and many other potent anthropogenic activities.
"I am fighting to save our planet and our future"
— COP26 (@COP26) November 2, 2020
Listen to 9 year old climate activist @LicypriyaK discuss the devastating effects of #ClimateChange in India & South Asia 👇
With one year to go until #COP26, we must all come #TogetherForOurPlanet. 🌏#COP26Ambition pic.twitter.com/FwKq5yIAZe
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has projected and reported that global warming is likely to lead to more frequent and severe heat waves, heavier precipitation in the Himalayan region and other parts of South Asia, and more intense storms and hurricanes. Additionally, warming temperatures can lead to sea level rise, which can flood coastal areas and damage infrastructure.
It is evident from last many years hat the floods are very frequent and very disastrous like the recent floods in Pakistan. The country has a long history of flooding, and climate change is expected to make these events more frequent and severe in the future. Heavy monsoon rains, melting Himalayan glaciers, and sea level rise are all climate change-driven factors that contribute to flooding in Pakistan. Floods led a devastating impact on communities, causing damage to infrastructure, homes, and crops, as well as displacement of people and loss of life.
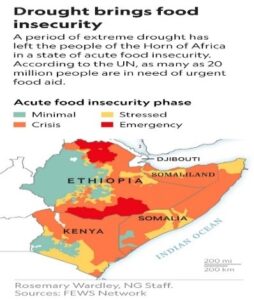 Climate change also causes the melting of ice sheets and glaciers, which contribute to sea level rise and disrupt ocean currents, which has a ripple effect on weather patterns around the world. Climate change also exacerbates existing problems such as air pollution and can make it harder to grow food and access fresh water, which can increase the risk of hunger and disease like in African countries.
Climate change also causes the melting of ice sheets and glaciers, which contribute to sea level rise and disrupt ocean currents, which has a ripple effect on weather patterns around the world. Climate change also exacerbates existing problems such as air pollution and can make it harder to grow food and access fresh water, which can increase the risk of hunger and disease like in African countries.
As many as 20 million people in African countries are facing drought conditions in the eastern Horn of Africa which has led to extreme hardship and food shortages for millions of people. The failure of three consecutive rainy seasons due to deadly climate change has resulted in a severe drought, leaving crops and livestock without sufficient water and food. This has led to food insecurity and malnutrition, particularly in vulnerable communities. The situation is further exacerbated by ongoing conflict, displacement, and economic challenges in the affected countries.
The floods across South Asia are a devastating reminder of how vulnerable the region is to climate change - impacting people’s human rights to housing, livelihoods and even life. pic.twitter.com/BdrUYg9vED
— Amnesty International South Asia (@amnestysasia) August 28, 2020
In the recent past, the region has been hit by several devastating climate-related events, such as the 2019 monsoon floods in India, Nepal, and Bangladesh that affected around 18 million people, caused widespread damage and displacement and killed hundreds of people. Monsoons in 2020 and 2021 also had a severe impact in India, Bangladesh and Pakistan, and other countries and are still unstoppable.
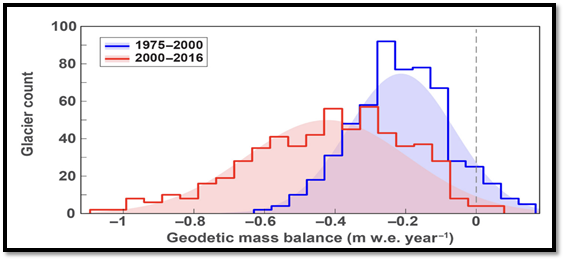
The region (South Asia) is home to some of the largest glaciers outside the polar regions, including the Himalayan, Karakoram, and Hindu Kush Mountain ranges. These glaciers are sensitive to changes in temperature and precipitation and are experiencing significant melting as a result of global warming.
The melting of glaciers in the region has a number of impacts, including sea level rise, changes in water availability, and increased risk of flooding and landslides. As glaciers melt, they release large amounts of water into rivers, which cause flash floods and damage to infrastructure as is prevalent nowadays in South Asian countries. Melting glaciers can also lead to changes in water availability for irrigation and hydroelectric power, which can have a significant impact on agriculture and energy production in the region.
Climate change is a global issue that needs to be addressed to mitigate its impacts on natural and human systems. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adapting to the changing climate, and protecting vulnerable communities. Addressing climate change requires a multifaceted approach that involves changes in policy, technology, and behavior at the global, national, and local levels.
As a result, there are a number of international and national efforts underway to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. These include the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), which is working to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
The World has a «third pole» and its melting fast.
— Erik Solheim (@ErikSolheim) August 17, 2020
Himalayan glaciers have lost a third of the ice since 1975 due to global warming. It is extremely dangerous for life along major Asian rivers in India 🇮🇳, China 🇨🇳 and beyond.…
pic.twitter.com/1x9zUWdzGS
It’s important to note that climate change is a global issue that requires a global effort, and requires actions from individuals, governments, and businesses to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the changes that are already happening. It is also necessary to play your part at the individual level to fight for climate justice. Effective implementation of adaptation and mitigation measures is required with immediate effect. There are various ways that we can choose now to fight global climate change and its adverse impacts and including,
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: This can be done by using renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, rather than fossil fuels, and by implementing energy efficiency measures.
- Planting Trees: Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it as carbon in their biomass, leaves, branches, and roots.
- Invest in clean energy: Governments and companies can invest in clean energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels.
- Using Public Transportation: Using public transportation, cycling or walking instead of using a car.
- Supporting carbon pricing: Carbon pricing is a policy that puts a price on greenhouse gas emissions, making it more expensive to pollute.
- Supporting Climate-smart agriculture: Climate-smart agriculture is an approach that helps farmers adapt to the effects of climate change, while also reducing emissions and improving food security.
- Recycling and reducing waste: Landfills are a significant source of methane emissions, so reducing waste and recycling more can help to reduce emissions.
- Supporting conservation: Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems, such as forests and wetlands, can help to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in biomass and soils.
- Supporting reforestation: Planting trees and restoring forests can help to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in biomass and soils.